Arcing Approach
Arcing approaches provide the safe and expeditious transition from the en-route environment to the terminal area.
Introduction
- An arcing approach is a type of instrument approach where the aircraft flies a set radius around the NAVAID in order to intercept a final approach course inbound
Arc Methods
- Fly the arc via GPS:
- Simply follow the indications on the GPS
- Fly 10, twist 10:
- Once established on the arc, twist the HSI 10 degrees off (in direction of turn-twist left, turn left or twist right, turn right)
- Fly until HSI centers then turn 10 degrees along the arc and twist another 10 degrees
- Continue doing this until you reach the lead turn radial to turn on the final approach course
- Essentially, the pilot is turning the arc into segments
Arc Approach Procedure
- Listen to ATIS or tower for landing runways and possible equipment outages
- Request approach from Air Traffic Control
- Tune and identify the NAVAID and DME, as appropriate
- Verify that the HI or HSI is aligned with the magnetic compass
- Fly ATC instructions, which will be vectors for final (skip ahead) or vectors for the initial approach fix (IAF)
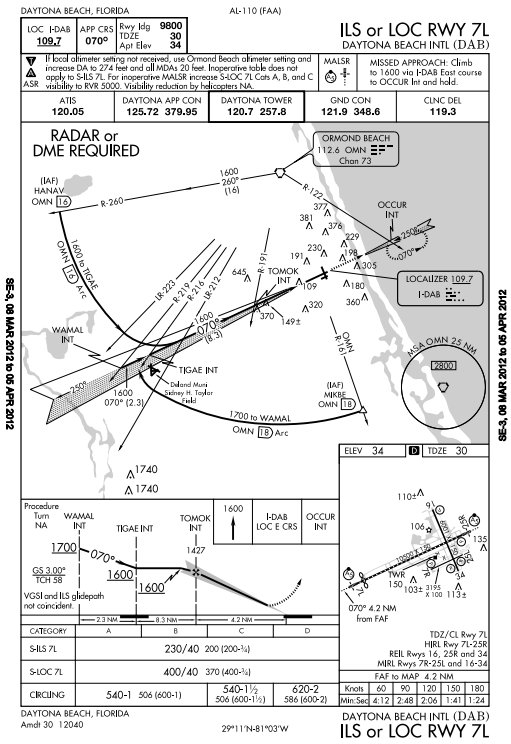
- Looking at the ILS/LOC 7L, you will proceed to HANAV if from the north or MIKBE if from the south
- Review the approach plate and give an approach brief
- Determine whether to join the arc with a left or right turn
- Join the arc by anticipating turn radius
- Intercepting the arc from a radial (90°), use 0.5-1% of the ground speed
- If intercepting at less than an 90° degree angle, use less lead
- Comply with all altitude restrictions
- Note the distance after the turn is completed:
- If the DME is 0.1 greater than the arc, turn 10° toward the arc
- If the DME is 0.1 less than the arc, maintain your current heading until the DME increases to the assigned DME distance, then turn 10deg; toward the arc
- To help maintain positional orientation and situational awareness, use the OBS to determine your position along the arc
- Complete the descent flow/checklists
- Fly the arc until your lead radial for the final approach course
- Lead radial is determined using your arc distance and Ground Speed (GS):
- 60 ÷ Arc Distance x 1% of GS
- Example: If the arc is 16 NM, flying at 80 knots ground speed:
- 60 ÷ 16 x .8 = 3 radials
- Lead radial is determined using your arc distance and Ground Speed (GS):
- Join the final approach course and center up the CDI
- Comply with all altitude restrictions
- At the Final Approach Fix (FAF), report:
- "[Facility-Tower], [Callsign], final approach fix, gear 3 down and locked"
- Descend to Minimum Descent Altitude (MDA), complying with altitude restrictions
- At the missed approach point, execute the missed approach instructions
Arc Approach Airman Certification Standards
Conclusion
- Remain mindful that performance calculations are usually more optimistic than actual performance
- Consider actual versus realized performance when doing any performance calculations
- Consider practicing maneuvers on a flight simulator to introduce yourself to maneuvers or knock off rust
- Still looking for something? Continue searching: