Reporting Procedures
Reports are notifications given by a pilot to ATC to aid in controller situational awareness when RADAR may not be available.
Introduction to Reporting
- The safety and effectiveness of traffic control depend to a large extent on accurate position reporting.
- To provide the proper separation and expedite aircraft movements, ATC must be able to make accurate estimates of the progress of every aircraft operating on an IFR flight plan.
Position Identification
- When making a position report while passing a VOR radio facility, the time reported should be the time at which the "to/from" indicator first completes its reversal.
- When making a position report while passing a facility by means of an airborne ADF, the time reported should be the time at which the indicator makes a complete reversal.
- When an aural or a light panel indicates the time passing a reporting point, such as a fan marker, Z marker, cone of silence, or intersection of range courses, pilots must note the time the signal is first received and again when it ceases.
- The mean of these two times should then be taken as the actual time over the fix.
- If given a position with respect to distance and direction from a reporting point, pilots must compute these values as accurately as possible.
- Except for terminal area transition purposes, position reports or navigation with reference to aids not established for use in the structure in which flight is being conducted will not normally be required by ATC.
Position Reporting Points
- CFRs require pilots to maintain a listening watch on the appropriate frequency and to furnish position reports passing certain reporting points.
- Reporting points are shown on enroute charts.
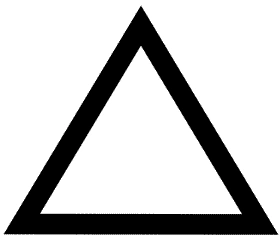
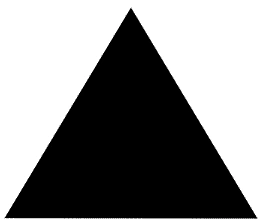
- Compulsory reporting points are a solid triangle. [Figure 1]
- Non-compulsory reporting points are open triangles, which are only required when requested by ATC. [Figure 2]
- A list of reporting points can be found within Federal Aviation Administration Order (7400.9) Airspace Designations and Reporting Points.
- Reports passing an "on request" reporting point are only necessary when requested by ATC.
-
Position Report Items:
- Identification.
- Position.
- Time.
- Altitude or flight level (include actual altitude or flight level when operating on a clearance specifying VFR-on-top).
- Type of flight plan (not required in IFR position reports made directly to ARTCCs or approach control).
- ETA and name of next reporting point.
- The name only of the next succeeding reporting point along the route of flight.
- Pertinent remarks.
Reporting Requirements
-
Flights Along Airways or Routes:
- Required by all flights, regardless of altitude, including those operating in accordance with an ATC clearance specifying "VFR-ON-TOP," over each designated compulsory reporting point along the route being flown.
-
Flights Along a Direct Route:
- Regardless of the altitude or flight level being flown, including flights operating in accordance with an ATC clearance specifying "VFR-on-top," pilots must report over each reporting point used in the flight plan to define the route of flight.
- This scenario can be especially applicable during an ATC-Alert, ATC-Limited, or ATC-Zero situation.
-
Flights in a Radar Environment:
- When informed by ATC that their aircraft are in "radar contact," pilots should discontinue position reports over designated (explicitly requested) reporting points.
- They should resume normal positioning reporting when ATC advises "radar contact lost" or "radar service terminated."
- Controllers attempting to radar contact an aircraft will assign a specific squawk or ask for an IDENT.
-
Flights in an Oceanic (Non-radar) Environment:
- Pilots must report over each point used in the flight plan to define the route of flight, even if the point is depicted on aeronautical charts as an "on request" (non-compulsory) reporting point.
- For aircraft providing automatic position reporting via an Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Contract (ADS-C) logon, pilots should discontinue voice position reports.
- ATC will inform pilots that they are in "radar contact:"
- When their aircraft is initially identified in the ATC system; and.
- When radar identification is reestablished after radar service has been terminated or radar contact lost:
- After being advised that the controller has established radar contact, this fact will not be repeated to the pilot when handed off to another controller. At times, the aircraft identity will be confirmed by the receiving controller; however, this should not be construed to mean that radar contact was lost. The identity of transponder-equipped aircraft will be confirmed by asking the pilot to "ident," "squawk standby," or to change codes. Aircraft without transponders will be advised of their position to confirm identity. In this case, the pilot is expected to advise the controller if in disagreement with the position given. Any pilot who cannot confirm the accuracy of the position given because of not being tuned to the NAVAID referenced by the controller should ask for another radar position relative to the tuned-in NAVAID.
Required Reports
- The following reports are to be made to ATC or FSS facilities without a specific ATC request, remembered with the acronym "MARVELOUS VFR C500:"
- Missed approach execution (request clearance for specific action; i.e., to alternate airport, another approach, etc.).
- Airspeed changes in the average true airspeed (at cruising altitude) when it varies by 5% or 10 knots (whichever is greater) from that filed in the flight plan.
- Reaching a holding fix or point to which cleared (report the time and altitude or flight level).
- VFR on top altitude changes.
- Estimate correction at any time it becomes apparent that an estimate as previously submitted is in error in excess of 2 minutes (non-radar).
- For flights in the North Atlantic (NAT), a revised estimate is required if the error is 3 minutes or more.
- Leaving any assigned holding fix or point.
- There exists an exception for pilots of aircraft involved in instrument training at military terminal area facilities when radar service is being provided.
- Outer marker or fix inbound (non-radar).
- Unforecast, or hazardous conditions encountered, or hazardous conditions which have been forecast, are expected to forward a report, such as weather, to ATC (non-radar).
- Safety of flight-related information.
- Vacating any previously assigned altitude or flight level for a newly assigned altitude or flight level.
- Final approach fix inbound on final approach (nonprecision approach) used in place of the outer marker inbound on final approach (precision approach) (non-radar).
- Radio or navigation failures.
- Includes any loss, in controlled airspace, of VOR, TACAN, ADF, low frequency navigation receiver capability, GPS anomalies while using installed IFR-certified GPS/GNSS receivers, complete or partial loss of ILS receiver capability, or impairment of air/ground communications capability.
- Reports should include aircraft identification, equipment affected, the degree to which the capability to operate under IFR in the ATC system is impaired, and the nature and extent of assistance desired from ATC.
- Other equipment installed in an aircraft may effectively impair safety and/or the ability to operate under IFR.
- If such equipment (e.g., airborne weather radar) malfunctions and, in the pilot's judgment, either safety or IFR capabilities are affected, it must be reported.
- When reporting GPS anomalies, include the location and altitude of the anomaly.
- Be specific when describing the location and include the duration of the anomaly if necessary.
- Compulsory reporting points (non-radar).
- 500 FPM climb/descent rate is not attainable.
- In summary, reports at all times:
- Missed approach.
- Airspeed ±10 knots or 5% change of filed TAS.
- Reaching a holding fix (time and altitude).
- VFR on top altitude changes.
- Leaving a holding fix.
- Safety of flight.
- Vacating an altitude or flight level.
- Radio or navigation failure.
- 500 FPM climb or descent rate not obtainable.
- Reports in a non-radar environment:
- ETA change of ±2 or 3 minutes (as applicable).
- Outer marker inbound.
- Unforecasted weather or encountering forecasted hazardous conditions.
- Final approach fix inbound.
- Compulary reporting points.
Inflight Monitoring and Reporting
- Pilots are encouraged to monitor 121.5 MHz and/or 243.0 MHz while inflight to assist in identifying possible emergency ELT transmissions. On receiving a signal, report the following information to the nearest air traffic facility:
- Your position when you first heard the signal.
- Your position at the time the signal was last heard.
- Your position when at maximum signal strength.
- Your flight altitudes and the frequency at which the emergency signal was heard (121.5 MHz or 243.0 MHz).
- If possible, positions should be given relative to a navigation aid.
- If the aircraft has homing equipment, provide the bearing to the emergency signal with each reported position.
Air Traffic Control Reporting Requirements
- Internal to Air Traffic Control procedures are Mandatory Occurrence Reports, or MORs.
- The process, in most cases, is transparent to pilots.
- MORs are guided by JO 7210.632A, Air Traffic Organization Occurrence Reporting.
- All employees must ensure that the following occurrences, of which they are aware through either direct involvement or observation, are reported:
- Airborne Loss of Separation.
- Unauthorized Unmanned Aircraft System (UAS).
- Airport Surface Loss of Separation.
- Terrain/Obstruction Loss of Separation.
- Airborne Air Traffic Control Anomalies (Airspace/Altitude/Route/Speed) Not Involving a Loss of Separation.
- Airport Environment issues.
- Oceanic Environment issues.
- Communication issues.
- Emergency or In-Flight Hazard.
- Inquiries from external entities.
- Instances that involve a deviation by the pilot may result in ATC stating "possible pilot deviation" with the request to call a number provided.
Reporting Conclusion
- In addition to reporting related to flight operations, pilots must be aware that any significant incident on their record may impact their eligibility to execute their privileges, for example, a DUI/DWI charge.
- Still looking for something? Continue searching:
Reporting References
- AOPA - Training Tip: In Guard We Trust.
- Federal Aviation Administration - Pilot/Controller Glossary.
- Aeronautical Information Manual (5-3-2) Position Reporting.
- Aeronautical Information Manual (5-3-3) Additional Reports.
- AOPA - For The Record: Abnormal Findings.
- CFI Notebook.net - Air Route Traffic Control Center (ARTCC).
- CFI Notebook.net - IFR Flight Plan.
- CFI Notebook.net - Pilot Reports.
- CFI Notebook.net - Terminal Radar Approach Control (TRACON).
- Federal Aviation Administration Order (7400.9) Airspace Designations and Reporting Points.
- Federal Aviation Regulations (71.5) Reporting Points.
- Federal Aviation Regulations (Part 71 subpart H) Reporting Points.
- Federal Aviation Regulations (91.183) IFR Communications.
- Federal Aviation Regulations (91.187) Operation under IFR in controlled airspace: Malfunction reports.