All procedures are GENERALIZED.
Fly the maneuver in accordance with the Pilot Operating Handbook (POH)
and/or current Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
Stall/Aerobatic Checklist:
- Cockpit: Clear of lose objects
- Seat Belts: Locked and tight
- Autoignition/Fuel Pump: On
- Engine Instruments: Checked
- Report: Stall/aerobatic checklist complete
Additional Considerations:
- Ensure pockets are zipped and the map-case is secured to prevent loose items from going airborne
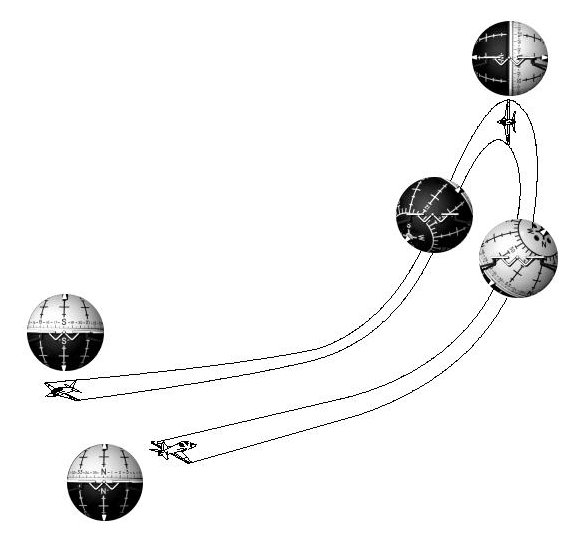
T-34C PROCEDURE:
- Give an instrument, gas, and position report (IGP)
- CONFIGURATION: aerobatic cruise
- Complete the stall/aerobatic checklist
- CODES: 4700
- Perform a clearing turn
- Successive wingovers, when continued without interruption, serve as clearing turns for the next series
- Roll out on or parallel to a section line
- Anticipate the section line to roll out on it vs. searching after your clearing turn
- Pick a reference point on the horizon, 90° to either side of the nose, in the direction you intend to perform the maneuver
- Recheck the wings level and clear the airspace above you
- ICS: "Entry altitude is..."
- Raise the exhaust stacks to the horizon and then start a roll towards the 90° checkpoint
- Control pitch and roll rate so as to reach:
- Nose: 45° up (aggressive at first)
- AoB: 45° ("Feels" like you need to put a lot more pitch input than AoB)
- Heading change: 45°
- Continue to roll towards:
- Speed: 90 KIAS
- AoB: 90°
- Heading change: 90° (do not exceed 90° AoB)
- Allow the nose to fall through the horizon, and then commence the recovery by smoothly rolling and pulling out of the diving turn
- The tendency is to recover AoB too fast, keep it slow
- After approximately 135 of turn:
- Nose: 45° down
- AoB: 45°
- Control the pitch and roll rate so as to recover on the original altitude and reciprocal heading
- Repeat steps 6 through 8, performing the second wingover in the opposite direction
- Upon completion of the series, the aircraft should once again be established in level balanced flight, on the original heading and altitude
When the maneuver is completed at the same altitude it was initiated, there is a tendency to gain about 10 KIAS
Wingover Common Errors:
- Failure to adequately clear the area
Airman Certification Standards:
Conclusion:
- Consider actual versus realized performance when doing any performance calculations
- Consider practicing maneuvers on a flight simulator to introduce yourself to maneuvers or knock off rust
- Still looking for something? Continue searching: